The First Snapshot of Ubuntu 26.04 LTS Released!

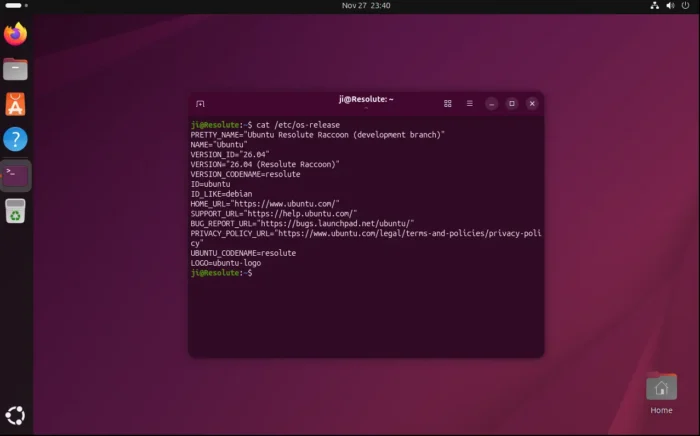
The first monthly snapshot release for Ubuntu 26.04 LTS was released yesterday morning (UTC time).
Ubuntu development team announced this development snapshot:
Hello everyone, I’d like to announce the first successful publication of the monthly snapshot – Resolute Snapshot 1. You can find the images on cdimage.ubuntu.com …
As you may know, Ubuntu 26.04 is the next Long Term Support (LTS) release with 5 years standard support until 2031, plus Expanded Security Maintenance (ESM) support until 2036, and security coverage (for paid customers) until 2041.
Ubuntu 26.04 will use GNOME 50 as default desktop environment. According to Linux Kernel history release date, it will perhaps be powered by Kernel 6.20 (or 7.0).
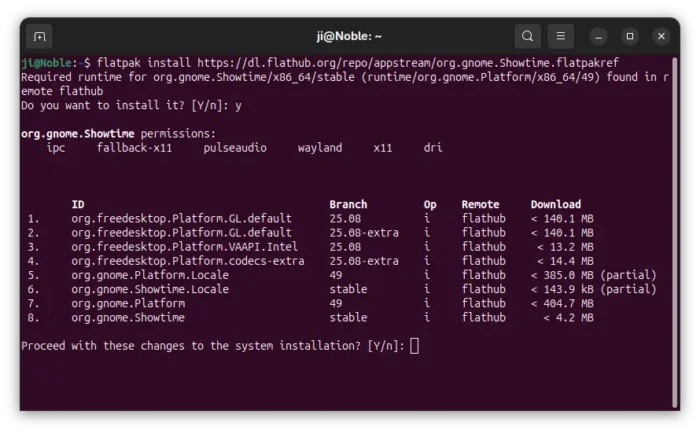
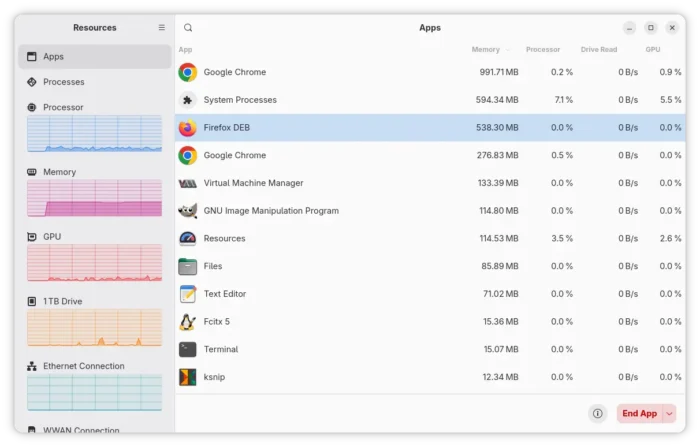
According to the road map, the 26.04 release will also introduced 2 new default applications. It will replace Totem with Gnome core Showtime video player, and replace Gnome System Monitor with Resources system monitor and task manager.
And, it will continue improving the performance and stability for Wayland on NVIDIA, unify the package management experience, and update Security Center with ability to re-encrypt a disk and manage Ubuntu Pro features.
At the moment, the 26.04 Snapshot 1 still has GNOME 49, Kernel 6.17, and most features are not completed yet. You may keep an eye on this on-going release note page for the recent changes.
Get Ubuntu 26.04 Snapshot 1
NOTE: This snapshot is a development release that’s NOT ready for production use!
The .iso images for Desktop and Server, as well as Netboot tarball and WSL image are available to download via the link below:
Don’t know why, but this snapshot does not provide the Desktop and Server image for amd64 (Intel/AMD platform) at the moment of writing.
Thanks to @Rodolfo, the iso images for amd64 (AMD/Intel platform) is available via the link below:
For non-GNOME users, the 26.04 snapshot 1 also includes the .iso images for all the 10 official flavors, which are available to download via the link below:
- EdUbuntu 26.04.
- KUbuntu 26.04.
- LUbuntu 26.04.
- Ubuntu Budgie 26.04.
- Ubuntu MATE 26.04.
- Ubuntu Unity 26.04.
- Ubuntu Cinnamon 26.04.
- UbuntuKylin 26.04.
- Ubuntu Studio 26.04.
- XUbuntu 26.04.
For current Ubuntu 25.10, it easy to upgrade to the new 26.04 Development release by first installing all updates:
sudo apt update && sudo apt full-upgrade
Restart if required, then run:
do-release-upgrade -d
For future releases, see the table below or the official release schedule.
| December 18, 2025 | Snapshot 2 |
| January 29, 2026 | Snapshot 3 |
| February 26, 2026 | Snapshot 4 |
| March 26, 2026 | Beta (mandatory) |
| April 16, 2026 | Final Freeze, Release Candidate |
| April 23, 2026 | Final Release |