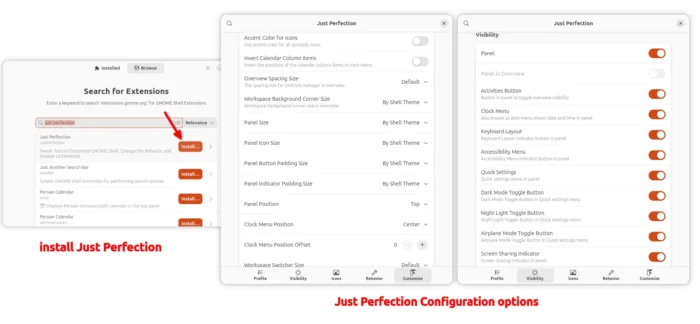
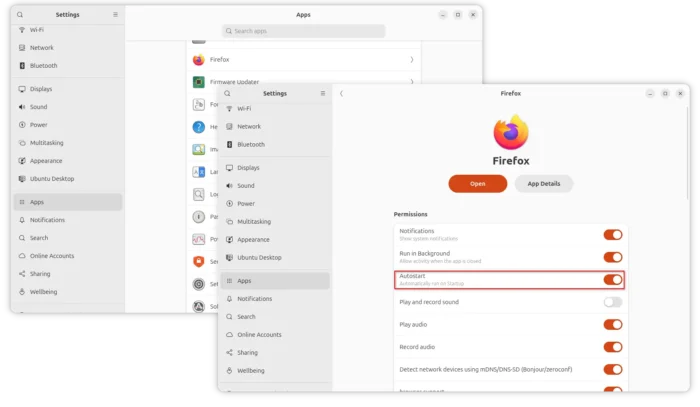
SuperTuxKart 1.5 Released! New Skins, Egg Hunts, & Supersampling
![]()
After almost three years of development, SuperTuxKart kart racing game finally released new major 1.5 version few days ago.
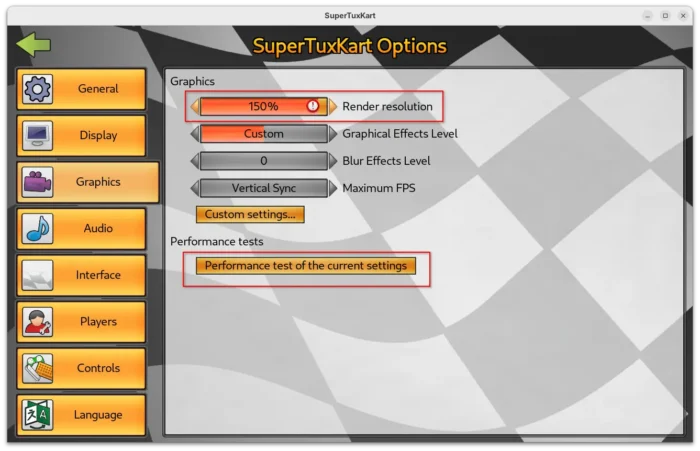
The new release of this game introduced Supersampling Anti-Aliasing (SSAA) support. Meaning that it can render game resolution higher than current screen size (even over maximum display resolution). It greatly improved the graphics quality, which is however extremely heavy that may lower frame rate.
You may enable this feature by going to “Graphics” setting page and set render resolution higher than 100%.
As you can see in the screenshot above, the setting page also added new “Performance test of the current settings” benchmark button. By clicking on the option, it starts a self-driving game with single loop track, and prints the performance test results, such as FPS, duration, and your current settings when it ends.
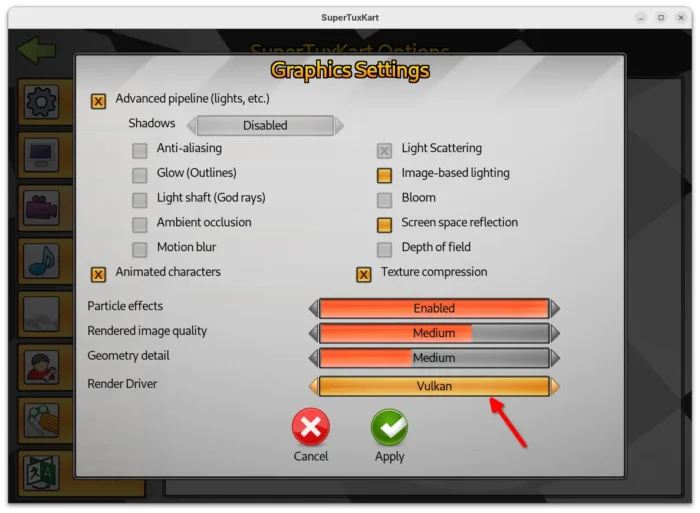
Besides that, the Vulkan support now goes stable. It added spotlight support and significant updates to the Vulkan renderer. And, user can now go to “Custom settings…” under Graphics to easily switch the render driver to Vulkan.
SuperTuxKart 1.5 as well improved level of details (LoD) and shadow mapping logic, which significantly reduce the occurrence of the sudden or abrupt appearance of game elements. And, it improved sound scale allowing headphone users to easily pick the ideal sound level.
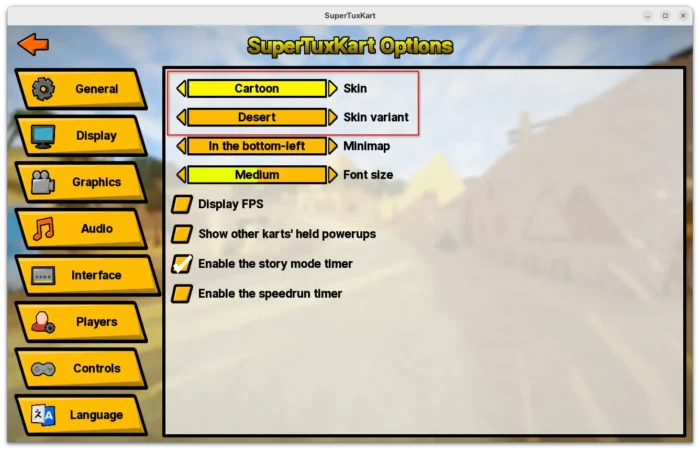
For the UI, the release added 6 new skins. The previous skins are now grouped as Classic with 5 variants, while a new Desert variant is added in this release. Cartoon theme now has five new variants, and each of them come with a background picture showing a scene from one of STK’s tracks.
Other changes in the release include three new egg hunts in Black Forest, Gran Paradisio Island and The Old Mine, and three new official fields in soccer mode. They are Oasis and XR-4R3N4 by CrystalDaEevee, and Hole Drop by CrystalDaEevee & Sven Andreas Belting.
There are as well following changes in the release:
- Move full-screen toogle, resoluation, and camera options into new Display setting page.
- Add “Screen space reflection” setting option.
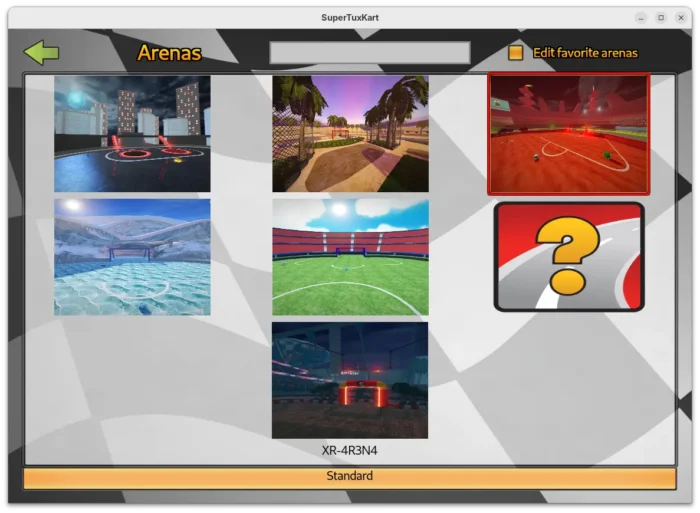
- Redesign the game mode and track selection page, reducing the need for scrolling.
- Add ability to mark tracks and karts as favorites.
- Add new nicer spawn animation for Parachute and Bubblegums.
- New spotlight lighting effect for karts in night tracks.
- New music for Las Dunas Arena and Las Dunas Soccer.
For more about the release, see the official announcement.
How to Install SuperTuxKart 1.5 in Ubuntu
The new release packages as well as the source code are available to download via the link below:
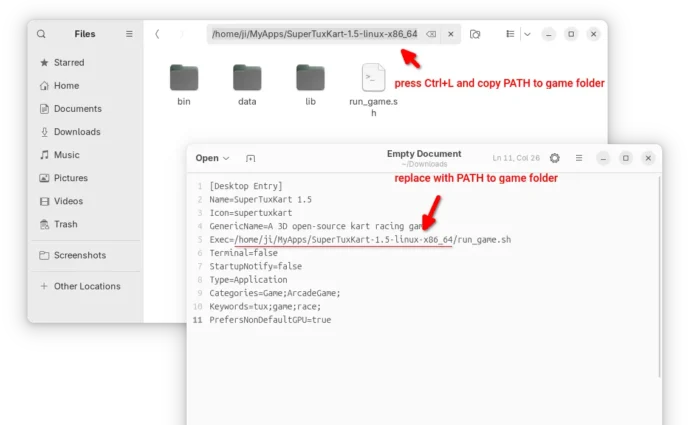
For Linux, it’s a portable tarball. Download and decompress it, then run the “run_game.sh” script to start the game.
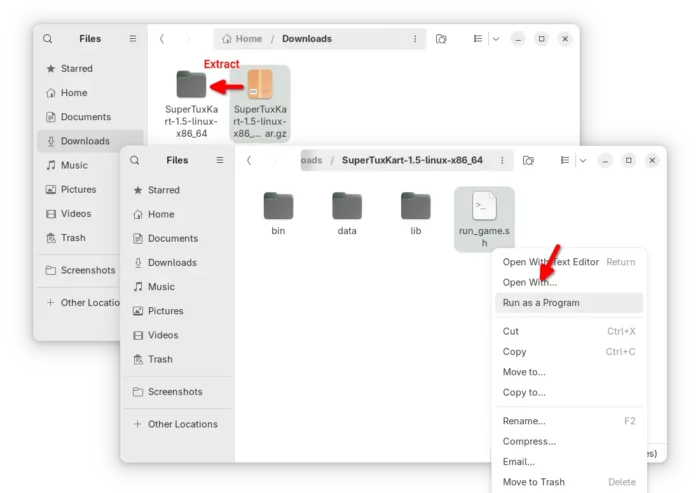
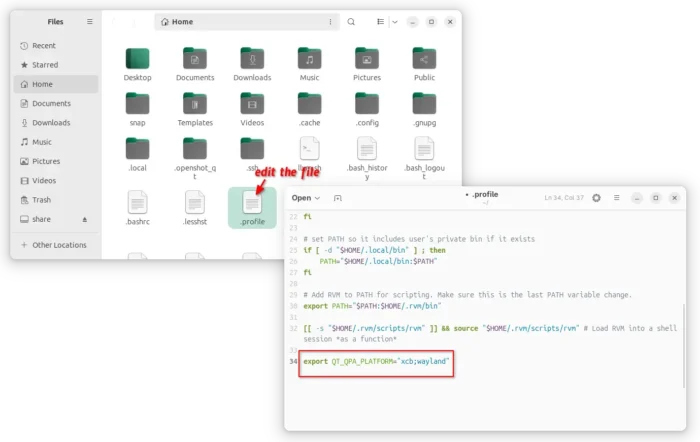
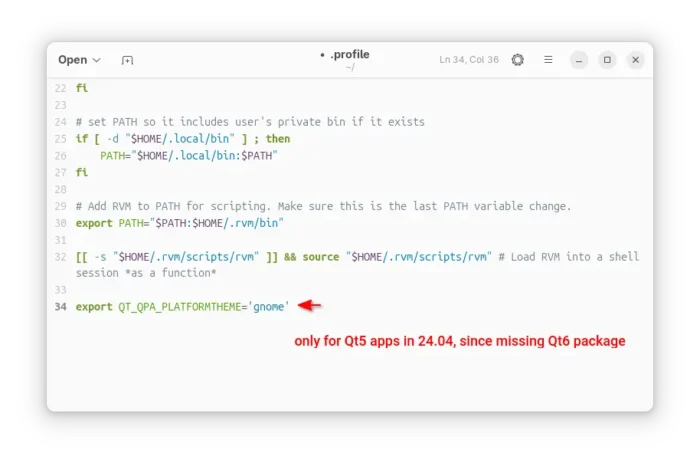
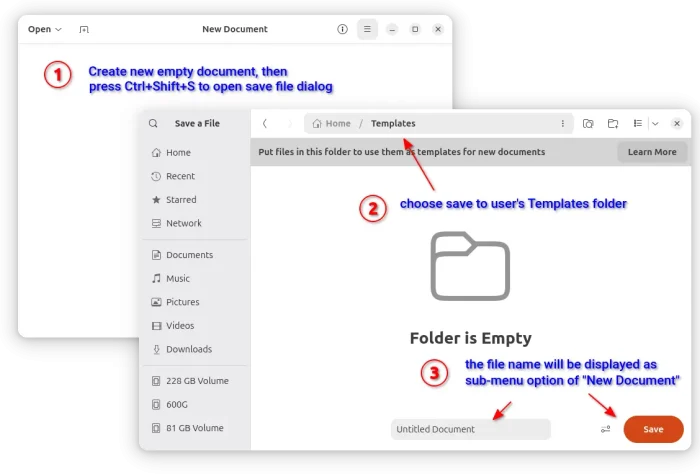
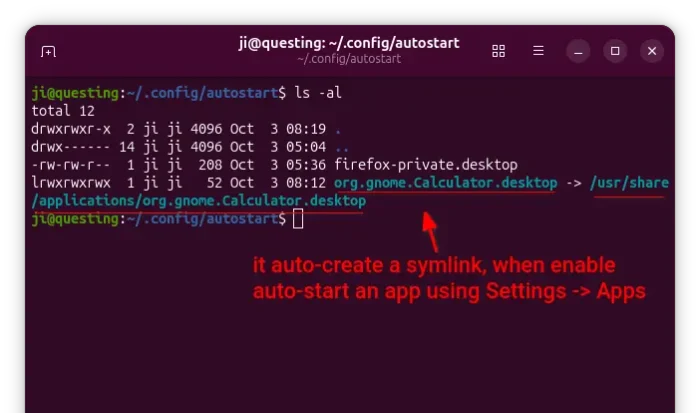
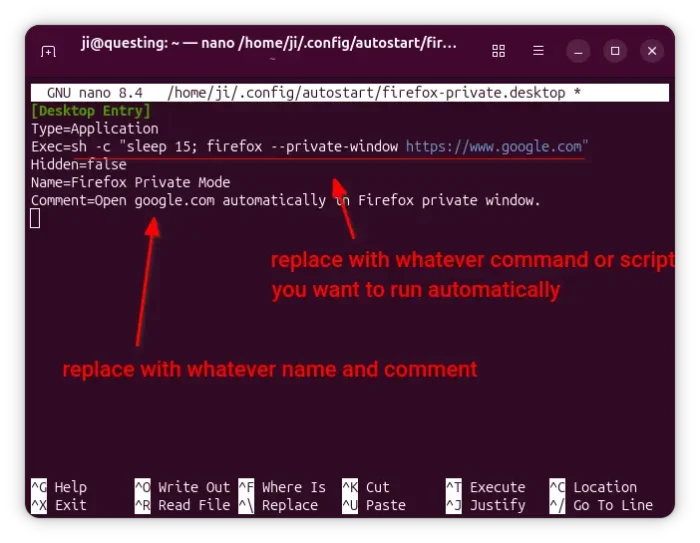
If you want to launch the game from app launcher (e.g., Gnome App Grid, overview search), then open Text Editor, create an empty document, then paste the following lines:
[Desktop Entry] Name=SuperTuxKart 1.5 Icon=supertuxkart GenericName=A 3D open-source kart racing game Exec=/home/ji/MyApps/SuperTuxKart-1.5-linux-x86_64/run_game.sh Terminal=false StartupNotify=false Type=Application Categories=Game;ArcadeGame; Keywords=tux;game;race; PrefersNonDefaultGPU=true
Here you need to replace the game PATH that’s in bold, according to where you saved the folder to.
In my case, I created “MyApps” folder in user home, and put all portable apps/games folders into there.
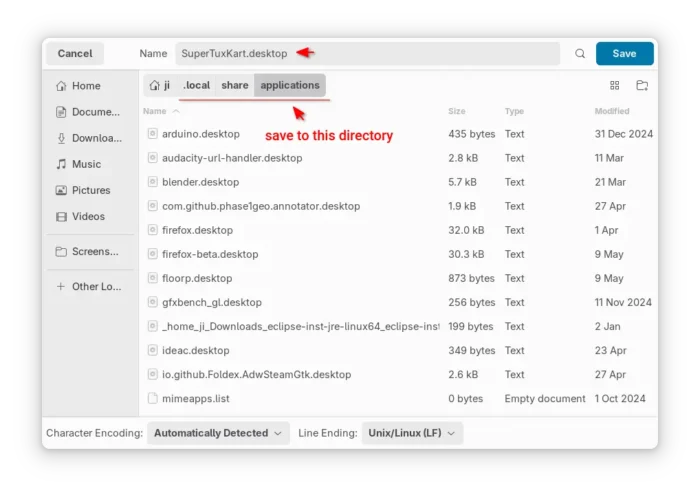
After that, save the file as “supertuxkart.desktop” into .local/share/applications directory. NOTE: .local is hidden by default, press Ctrl+H in file chooser dialog to view/hide it.
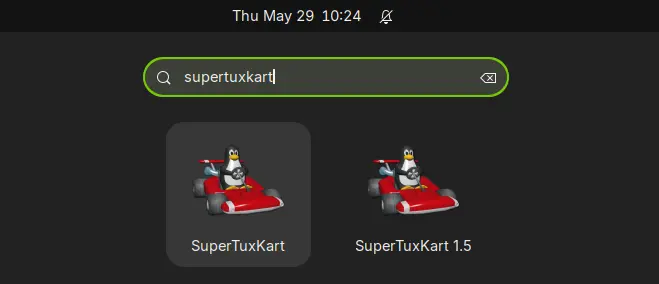
If everything goes well, you’ll be able to launch the game from start menu (or Gnome overview) few moments later.
Note for missing app icon, just grab one from the web, name it as supertuxkart (.PNG or .SVG), finally put it into .local/share/icons directory.
In my case, I have both SuperTuxKart 1.4 installed from system repository, and v1.5 via the Linux tarball. So, I have 2 game icons in launcher, but with different names.
Uninstall:
To uninstall the kart racing game installed via the steps above, simply delete the game folder using file manager.
Then, also delete the supertuxkart.desktop file from .local/share/applications, and delete the icons (if any) from .local/share/icons directory.